Proxmox VLAN Networking
May 20, 2024
What are VLANs and why should I use them?
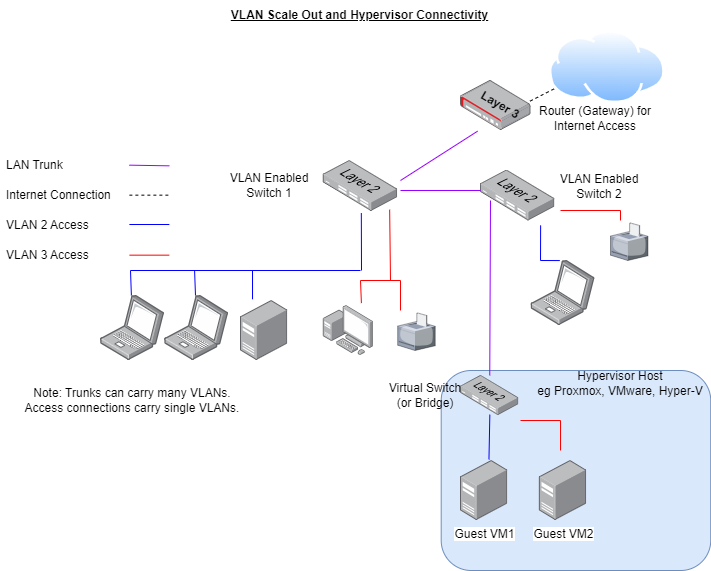
Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) allow the user a of network segmentation, which when combined with subnets, allow for a greater level of administrative control than a simple “flat LAN” single network approach.
Whilst you can split up network traffic using VLANs to physical devices, most hypervisors allow you extend the physical VLAN environment into the hypervisor.
Different hypervisors take different approaches to how this is implemented.
VLAN Configuration on Proxmox
In the case of Proxmox, this is a very simple setup.
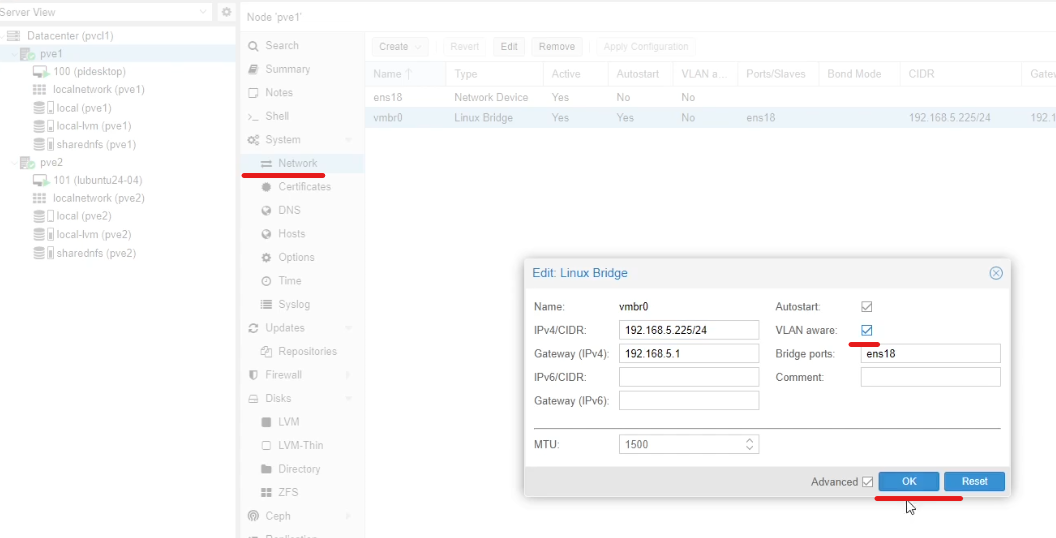
The network bridge device (physical network adapter) needs to be enabled for VLANs.
Go to the network settings for the host you want to configure, click on the bridge device you want to configure, click “edit”, then “VLAN aware” and then “OK”.
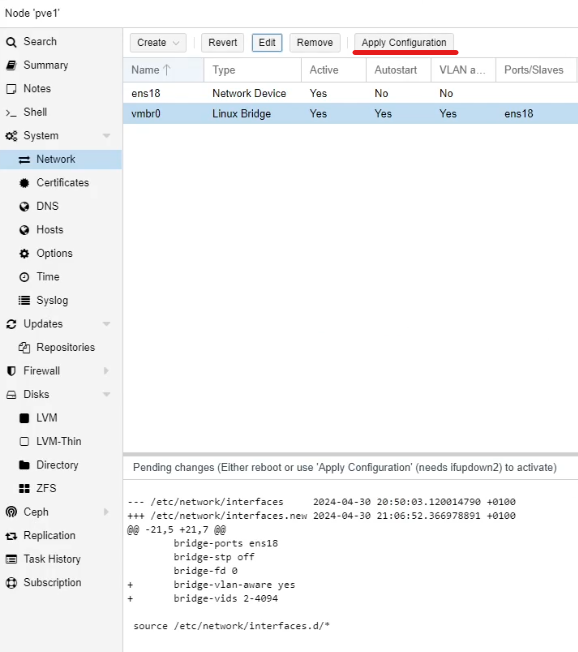
You next need to click “Apply Configuration”, and wait for the service to reload.
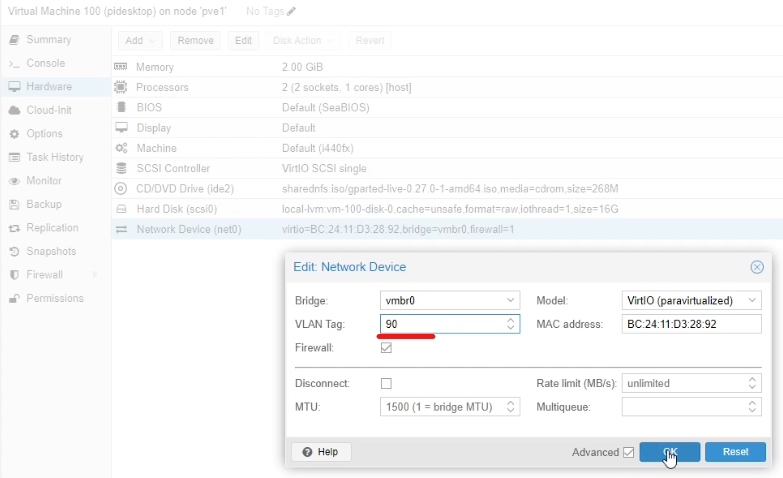
With this enabled, you then need to set the VM to use the correct bridge, and then set the VLAN tag to the VLAN you want to use, eg VLAN 90.
Video demonstration
The following video shows how to set up VLANs on Proxmox.
Comparison with VMWare and Hyper-V
Both VMware and Hyper-V take the approach of creating specific VLAN aligned switches for their implementation, whilst in the case of Hyper-V a specific VLAN tag is also needed on each VM.
The Proxmox implementation is simple to set up, and very easy to manage as there is no need to configure virtual switches on each host.
This makes Proxmox scaleable without needing the complexity of distributed switches or to ensure virtual switch naming schemas are consistent between hosts.
Important Note
A switched LAN is an OSI layer 2 implementation, and whilst it is possible to have overlapping subnets on different VLANs, in practice aligning subnets with VLANs allows for traffic to be routed (OSI layer 3) between the subnet/VLAN.
A router device is still needed to do this! VLANs alone will not let you move traffic from one subnet to another.